In this post, we’ll walk through how to build a simple yet robust RESTful API using ASP.NET Core and Oracle Autonomous Database. We’ll integrate Dapper for lightweight ORM functionality and demonstrate how to execute Oracle stored procedures efficiently.
Development Environment
- IDE: Visual Studio 2022 Community Edition
- Database: Oracle Autonomous Database (via Oracle Cloud)
- SQL Client: Oracle SQL Developer
- ORM: Dapper v2.0.123
- Oracle Driver: Oracle.ManagedDataAccess.Core v3.21.70
- Framework: ASP.NET Core 6+
Oracle Autonomous Database : https://www.oracle.com/autonomous-database/
Dapper: https://www.learndapper.com
Step 0: Create the Project for .NET Core Web API
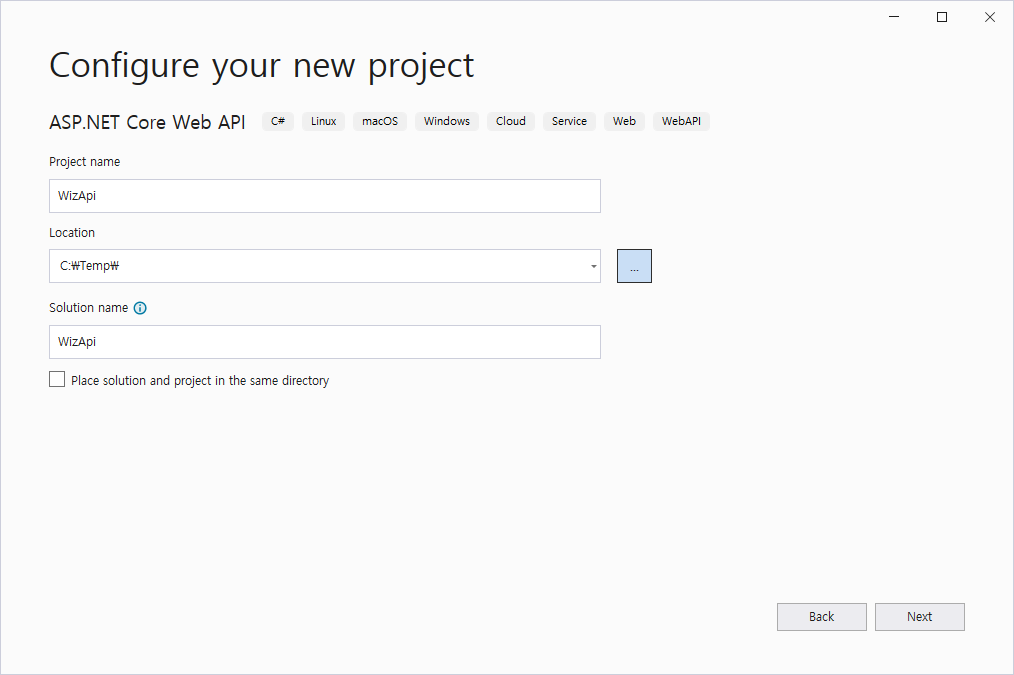
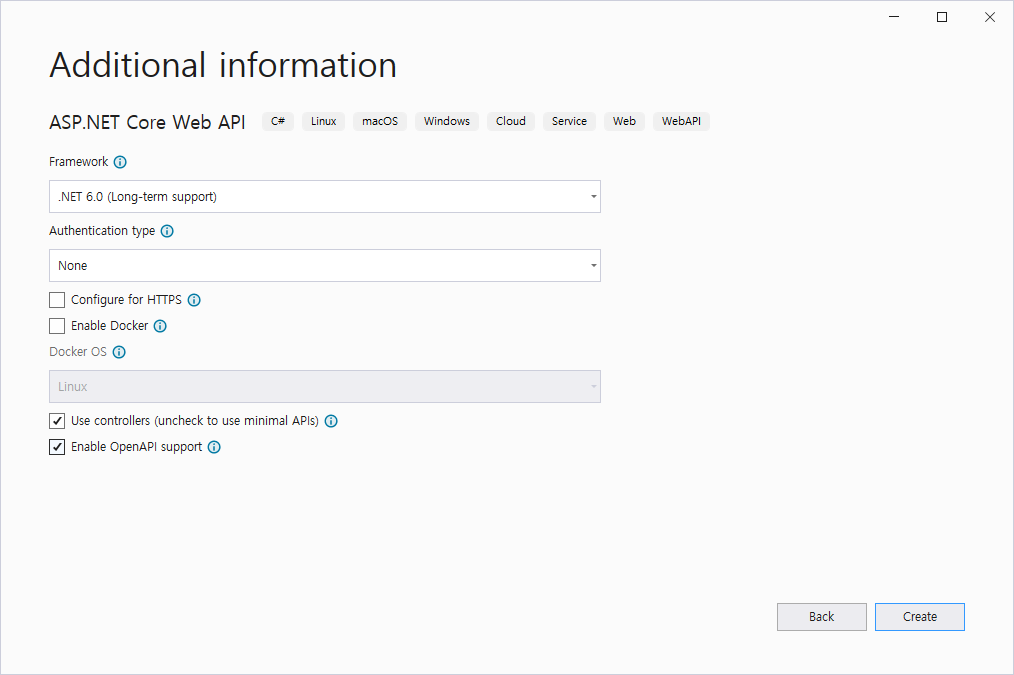
Step 1: Create the Database Table and Seed Sample Data
We begin by creating a TUSER table and populating it with sample data:
CREATE TABLE "USER"
(
"ID" NUMBER(10,0) GENERATED BY DEFAULT ON NULL AS IDENTITY
MINVALUE 1 MAXVALUE 9999999999999999999999999999 INCREMENT BY 1 START WITH 100 CACHE 20 NOORDER NOCYCLE,
"NAME" VARCHAR2(255 BYTE),
"AGE" NUMBER(5,0),
"REMARK" VARCHAR2(500 BYTE)
)Insert into TUSER(ID,NAME,AGE,REMARK) values (1000,'Spider-Man',17,'Alive');
Insert into TUSER(ID,NAME,AGE,REMARK) values (1001,'Black Widow',34,'Dead');
Insert into TUSER(ID,NAME,AGE,REMARK) values (1002,'Black Panther',38,'Alive');
Insert into TUSER(ID,NAME,AGE,REMARK) values (1003,'Iron Man',48,'Dead');
Insert into TUSER(ID,NAME,AGE,REMARK) values (1004,'Hulk',49,'Alive');
Insert into TUSER(ID,NAME,AGE,REMARK) values (1005,'Captain America',100,'Alive');
Insert into TUSER(ID,NAME,AGE,REMARK) values (1006,'Thor',1053,'Alive');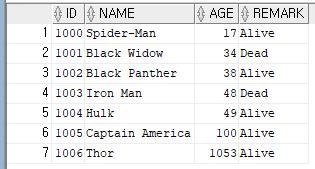
Step 2: Create Oracle Stored Procedures
We define two stored procedures: one for retrieving all users, and another for getting details by ID.
-- Get user list
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE USP_GET_TUSER_LIST (
P_CURSOR OUT SYS_REFCURSOR
) AS
BEGIN
OPEN P_CURSOR FOR
SELECT ID, NAME, AGE, REMARK FROM TUSER;
END;
-- Get user detail by ID
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE USP_GET_TUSER_DETAIL (
P_ID IN INT,
P_CURSOR OUT SYS_REFCURSOR
) AS
BEGIN
OPEN P_CURSOR FOR
SELECT ID, NAME, AGE, REMARK FROM TUSER WHERE ID = P_ID;
END;Step 3: Install nuget packages
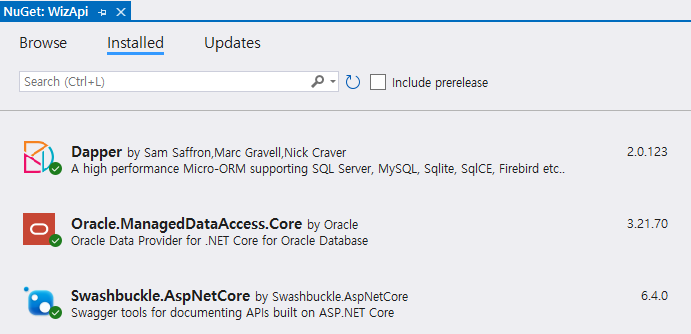
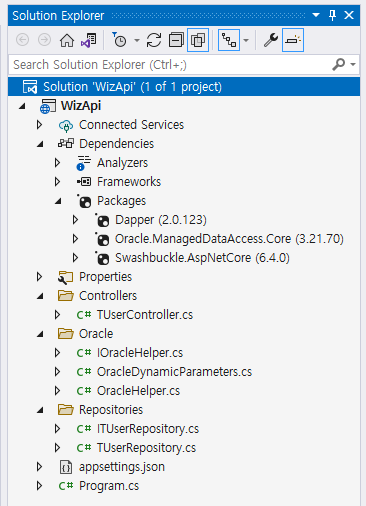
Step 4: Add Connection Settings in appsettings.json
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"ADBConnection": "User Id=[User ID]; Password=[Password]; Data Source=[TNS_NAME]; Connection Timeout=30;",
"WalletLocation": "C:\\TEMP\\Wallet_Location\\"
}
}Step 5: Create Oracle Helper Classes
Interface: IOracleHelper.cs
// IOracleHelper.cs
using System.Data;
namespace WizApi.Oracle
{
public interface IOracleHelper
{
IDbConnection GetConnection();
}
}Implementation: OracleHelper.cs
// OracleHelper.cs
using Oracle.ManagedDataAccess.Client;
using System.Data;
namespace WizApi.Oracle
{
public class OracleHelper : IOracleHelper
{
IConfiguration configuration;
public OracleHelper(IConfiguration _configuration)
{
configuration = _configuration;
}
public IDbConnection GetConnection()
{
var connectionString = configuration.GetSection("ConnectionStrings").GetSection("ADBConnection").Value;
var conn = new OracleConnection(connectionString);
return conn;
}
}
}Dynamic Parameters: OracleDynamicParameters.cs
// OracleDynamicParameters.cs
using Dapper;
using Oracle.ManagedDataAccess.Client;
using System.Data;
namespace WizApi.Oracle
{
public class OracleDynamicParameters : SqlMapper.IDynamicParameters
{
private readonly DynamicParameters dynamicParameters = new DynamicParameters();
private readonly List<OracleParameter> oracleParameters = new List<OracleParameter>();
public void Add(string name, OracleDbType oracleDbType, ParameterDirection direction, object value = null, int? size = null)
{
OracleParameter oracleParameter;
if (size.HasValue)
{
oracleParameter = new OracleParameter(name, oracleDbType, size.Value, value, direction);
}
else
{
oracleParameter = new OracleParameter(name, oracleDbType, value, direction);
}
oracleParameters.Add(oracleParameter);
}
public void Add(string name, OracleDbType oracleDbType, ParameterDirection direction)
{
var oracleParameter = new OracleParameter(name, oracleDbType, direction);
oracleParameters.Add(oracleParameter);
}
public void AddParameters(IDbCommand command, SqlMapper.Identity identity)
{
((SqlMapper.IDynamicParameters)dynamicParameters).AddParameters(command, identity);
var oracleCommand = command as OracleCommand;
if (oracleCommand != null)
{
oracleCommand.Parameters.AddRange(oracleParameters.ToArray());
}
}
}
}Step 6: Implement Repository Pattern
Interface: ITUserRepository.cs
// ITUserRepository.cs
namespace WizApi.Repositories
{
public interface ITUserRepository
{
object? GetTUserList();
object? GetTuserDetail(int tmpId);
}
}Implementation: TUserRepository.cs
// TUserRepository.cs
using Dapper;
using Oracle.ManagedDataAccess.Client;
using System.Data;
using WizApi.Oracle;
namespace WizApi.Repositories
{
public class TUserRepository : ITUserRepository
{
IOracleHelper oracleHelper;
public TUserRepository(IOracleHelper _oracleHelper)
{
oracleHelper = _oracleHelper;
}
public object? GetTuserDetail(int tmpId)
{
object? result = null;
try
{
var dyParam = new OracleDynamicParameters();
dyParam.Add("P_ID", OracleDbType.Int32, ParameterDirection.Input, tmpId);
dyParam.Add("P_CURSOR", OracleDbType.RefCursor, ParameterDirection.Output);
var conn = oracleHelper.GetConnection();
if (conn.State == ConnectionState.Closed)
{
conn.Open();
}
if (conn.State == ConnectionState.Open)
{
var query = "USP_GET_TUSER_DETAIL";
result = SqlMapper.Query(conn, query, param: dyParam, commandType: CommandType.StoredProcedure);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw;
}
return result;
}
public object? GetTUserList()
{
object? result = null;
try
{
var dyParam = new OracleDynamicParameters();
dyParam.Add("P_CURSOR", OracleDbType.RefCursor, ParameterDirection.Output);
var conn = oracleHelper.GetConnection();
if (conn.State == ConnectionState.Closed)
{
conn.Open();
}
if (conn.State == ConnectionState.Open)
{
var query = "USP_GET_TUSER_LIST";
result = SqlMapper.Query(conn, query, param: dyParam, commandType: CommandType.StoredProcedure);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw;
}
return result;
}
}
}Step 7: Configure dependencies (in Program.cs)
// Program.cs
using Oracle.ManagedDataAccess.Client;
using WizApi.Oracle;
using WizApi.Repositories;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var configuration = builder.Configuration;
OracleConfiguration.TnsAdmin = configuration.GetSection("ConnectionStrings").GetSection("WalletLocation").Value;
OracleConfiguration.WalletLocation = OracleConfiguration.TnsAdmin;
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IConfiguration>(configuration);
builder.Services.AddTransient<IOracleHelper, OracleHelper>();
builder.Services.AddTransient<ITUserRepository, TUserRepository>();
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();Step 8: Create API Controller
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using WizApi.Repositories;
namespace WizApi.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Produces("application/json")]
public class EmployeeController : Controller
{
ITUserRepository repository;
public EmployeeController(ITUserRepository _tUserRepository)
{
repository = _tUserRepository;
}
[HttpGet]
[Route("api/GetUserList")]
public ActionResult GetUserList()
{
var result = repository.GetTUserList();
if (result == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(result);
}
[HttpGet]
[Route("api/GetUserDetail/{tmpId}")]
public ActionResult GetUserDetail(int tmpId)
{
var result = repository.GetTuserDetail(tmpId);
if (result == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(result);
}
}
}🏁 Run and Test the Application
- Run the project in Visual Studio.
- Swagger UI will open at
http://localhost:<port>/swagger - Test your endpoints:
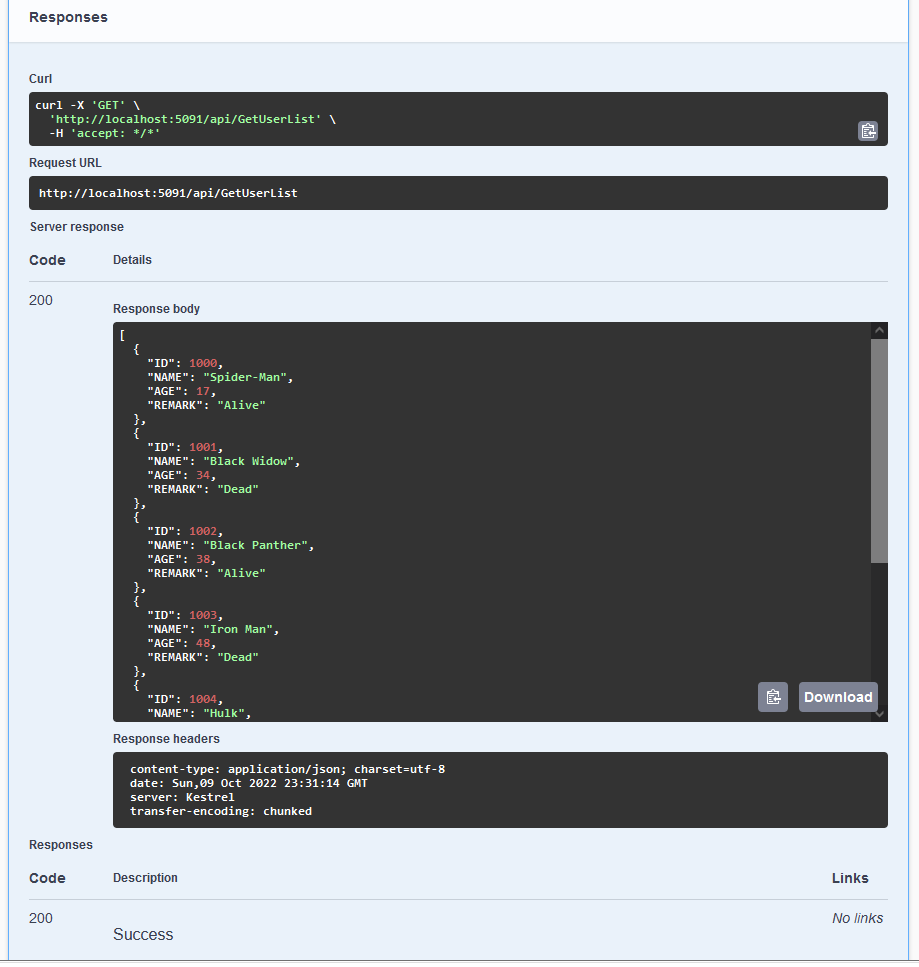
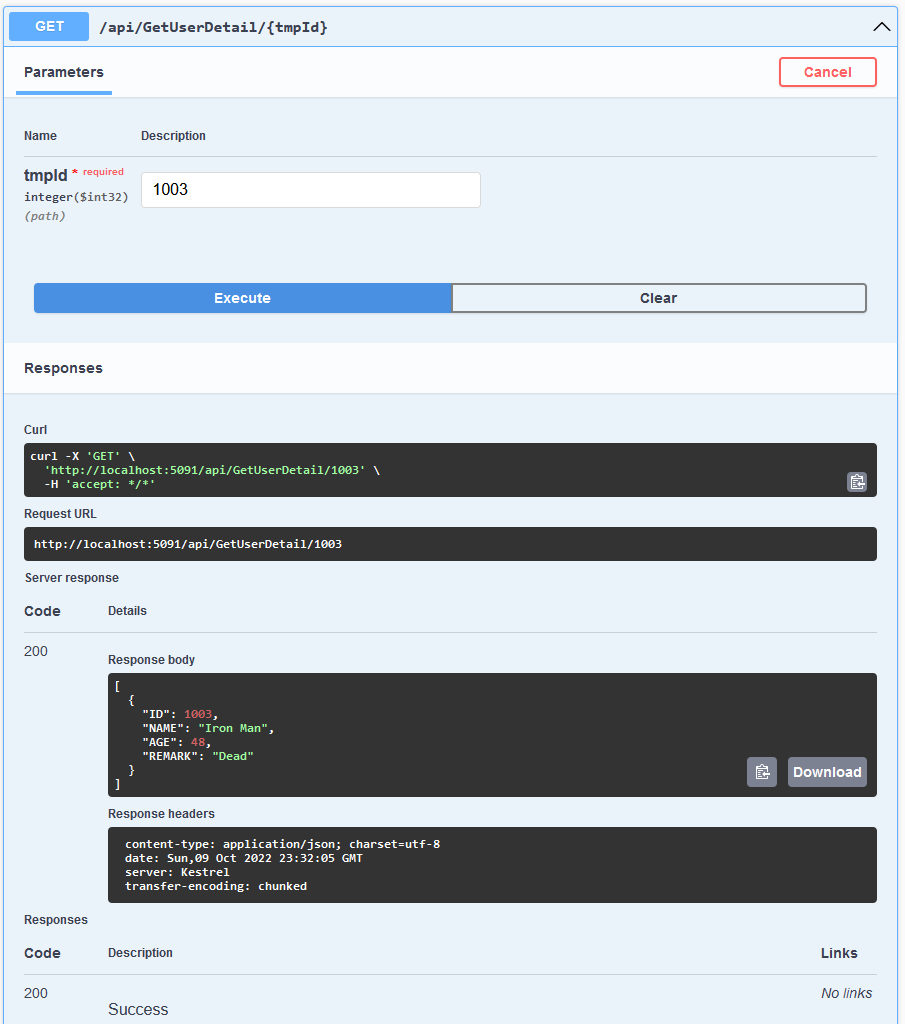
GET /api/Employee/GetUserListGET /api/Employee/GetUserDetail/{id}
✅ Summary
In this post, you learned how to:
- Connect .NET Core Web API to Oracle Autonomous Database using Dapper.
- Execute stored procedures with Oracle Ref Cursors.
- Organize code using the repository pattern.
- Set up a scalable, production-ready architecture with DI and configuration.
This is a solid foundation for building enterprise-grade applications that leverage Oracle databases with modern .NET APIs.
